Time is an important aspect of our lives, especially when it comes to planning trips, meetings, or conducting business in other countries. In this article, we will explore how time works in Cyprus, the time zone used, the seasonal time changes, and the differences in time with other countries. This will help tourists and business people better understand the time-related features of the island and avoid any time-related misunderstandings.
Contents
Current Time in Cyprus
Cyprus, located in the Eastern Mediterranean, uses Eastern European Time (EET) during the winter period, which corresponds to UTC+2. In the summer, from the end of March to the end of October, the island switches to daylight saving time — Eastern European Summer Time (EEST), which corresponds to UTC+3. This change happens annually on the last Sunday of March when the clocks are set forward by one hour. The return to winter time occurs on the last Sunday of October when the clocks are set back by one hour.
In the summer, this transition to daylight saving time helps make better use of daylight. Summer evenings in Cyprus remain brighter for longer, which creates favorable conditions for vacationers and tourists. Locals also appreciate this time, as the evening hours remain warm and comfortable for strolls or gatherings with friends on café terraces. The shift to daylight saving time primarily aims at saving electricity, making the island more eco-friendly.
During the winter, Cyprus returns to UTC+2, which is typical for much of Eastern Europe and some Middle Eastern countries. This standard time is also convenient for planning trips and business meetings, as it aligns with the schedules of many European countries during the winter period. It is important to note that Cypriots easily adapt to time changes, allowing them to maintain their daily rhythm without significant disruptions.
Time Zone of Cyprus
As mentioned earlier, Cyprus uses the EET time zone (UTC+2) in the winter and EEST (UTC+3) in the summer. This is a standard time system applied in several other Eastern European countries and the Eastern Mediterranean region, such as Finland, Greece, and Turkey. The transition to daylight saving time was introduced to conserve energy and make better use of natural light during the warmer months.
The time in Cyprus is synchronized with several major cities and regions in Europe, simplifying communication, business operations, and tourism. For people who frequently travel across Europe, the time zone in Cyprus will not pose significant challenges — the difference with Central Europe is only one hour (e.g., Germany and France), and with the UK, it is two hours in the summer and three hours in the winter.
Cyprus is situated at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and the Middle East, making it a convenient hub for international flights. It is important to note that despite its proximity to Turkey and the Middle East, the time zone in Cyprus differs from that of these countries. For example, Turkey does not switch to winter time and remains on UTC+3 throughout the year. This difference is important to consider when planning trips or business meetings with partners in this region.
Time Difference with Other Countries
The time difference between Cyprus and other countries varies depending on the time of year and the system of transitioning to daylight saving and winter time. Let’s look at a few examples of time differences with key countries and cities.
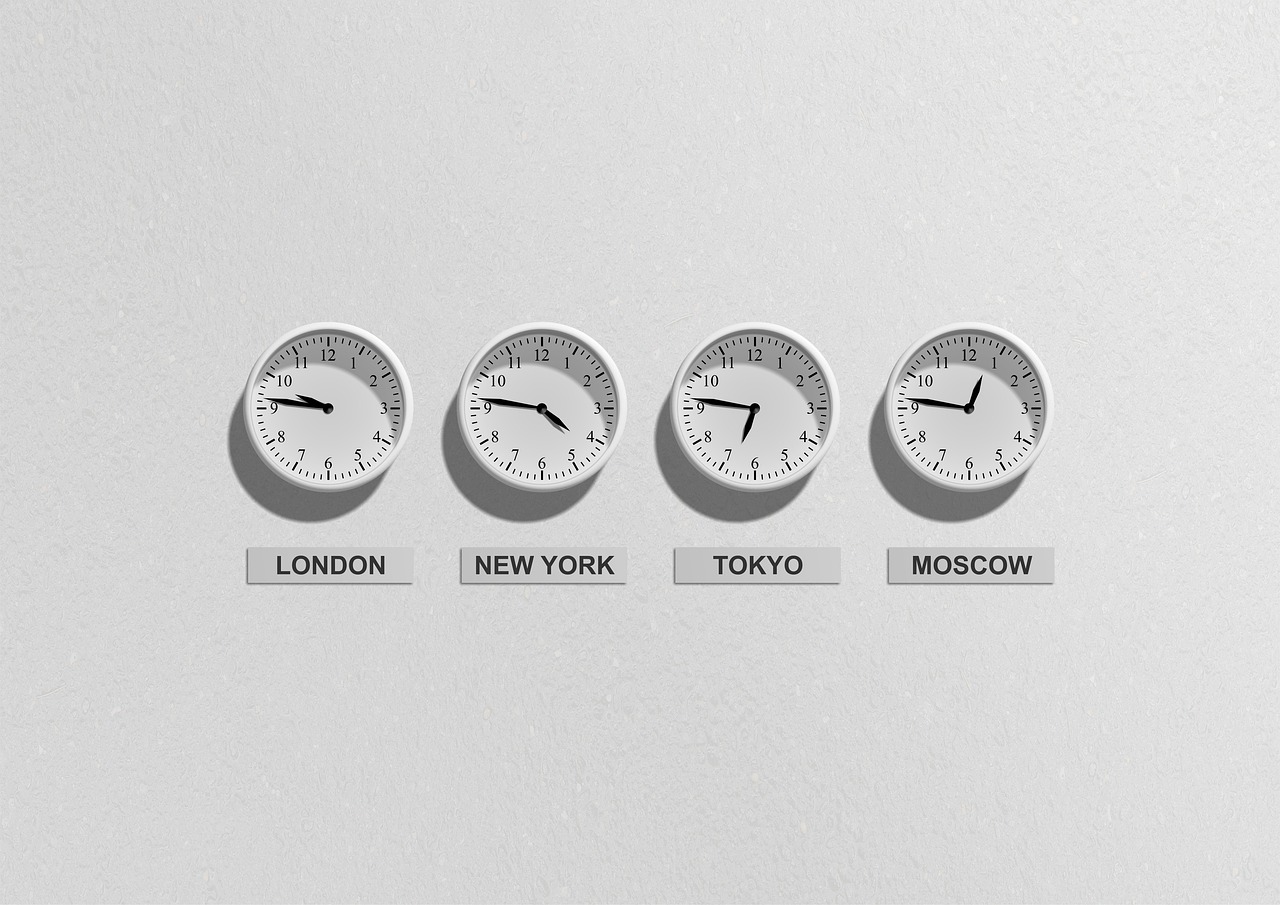
- Moscow, Russia: During the winter period, there is no time difference between Moscow and Cyprus, as Moscow also operates on UTC+3. In the summer, when Cyprus switches to daylight saving time, the time difference increases by one hour, with Cyprus being one hour ahead of Moscow.
- London, United Kingdom: In the winter, the time difference is two hours (Cyprus is ahead of London). In the summer, when both countries switch to daylight saving time, the difference decreases to three hours, as Cyprus moves to UTC+3 and London to UTC+1.
- New York, USA: In the winter, the time difference between New York and Cyprus is 7 hours, and in the summer, it is 6 hours. This is because the US also observes daylight saving time but follows its own schedule.
- Tokyo, Japan: The time difference between Cyprus and Tokyo remains consistent, at 7 hours in the winter and 6 hours in the summer, as Japan does not observe daylight saving time.
For travelers and people working with international partners, it is important to consider these differences when planning meetings or events. Even a small mistake in timing could lead to disrupted business negotiations or inconveniences during travel.
History of Time Changes in Cyprus
The history of daylight saving time in Europe dates back to the early 20th century. The system was first introduced during World War I to save fuel and make better use of daylight. Cyprus, being a British colony at the time, also adopted this system. After gaining independence in 1960, Cyprus continued the practice of daylight saving time, following European standards.
Initially, daylight saving time was introduced as a measure to save electricity in times of resource shortages. However, over time, the economic benefit of this system has become less noticeable, but it remains a habit and a measure that improves quality of life. In recent years, there have been active discussions in Europe about the necessity of maintaining daylight saving time. Some countries argue that this practice no longer serves a purpose and should be abolished.
At present, the European Union continues to debate reforms on abolishing seasonal clock changes, but Cyprus still follows this practice. How the situation will evolve in the future remains to be seen, but for now, the island’s residents continue to adjust their clocks twice a year.
Impact of Time Changes on Life and Tourism
Time changes in Cyprus have both positive and negative aspects. Daylight saving time, with its extended daylight hours, creates favorable conditions for tourism. Long, bright evenings allow travelers to enjoy the beaches and attractions for longer, which is one of the factors that draws tourists to the island during the summer season.
For local residents, daylight saving time also has its advantages: they can spend more time outdoors, enjoy evening walks, or relax with family. The energy savings, which historically were the main motivator for introducing daylight saving time, remain an important factor for the country.
However, switching between summer and winter time can create inconveniences for certain groups of people. For example, time changes can disrupt biological rhythms and cause temporary sleep disturbances. This is especially relevant for the elderly and children, who are more sensitive to changes in their daily routines. Nevertheless, most Cypriots adapt easily to these changes, and the inconveniences are usually short-lived.
Time in Cyprus, as in other European countries, is subject to seasonal changes. The use of standard and daylight saving time helps to make efficient use of daylight, which benefits both locals and tourists. Given the time difference with other countries, travelers and business people should plan their trips and meetings in advance to avoid any time-related inconveniences.
In the future, the practice of changing the clocks may be reconsidered, but for now, Cyprus remains committed to this tradition, offering its residents and visitors a comfortable experience throughout the year.