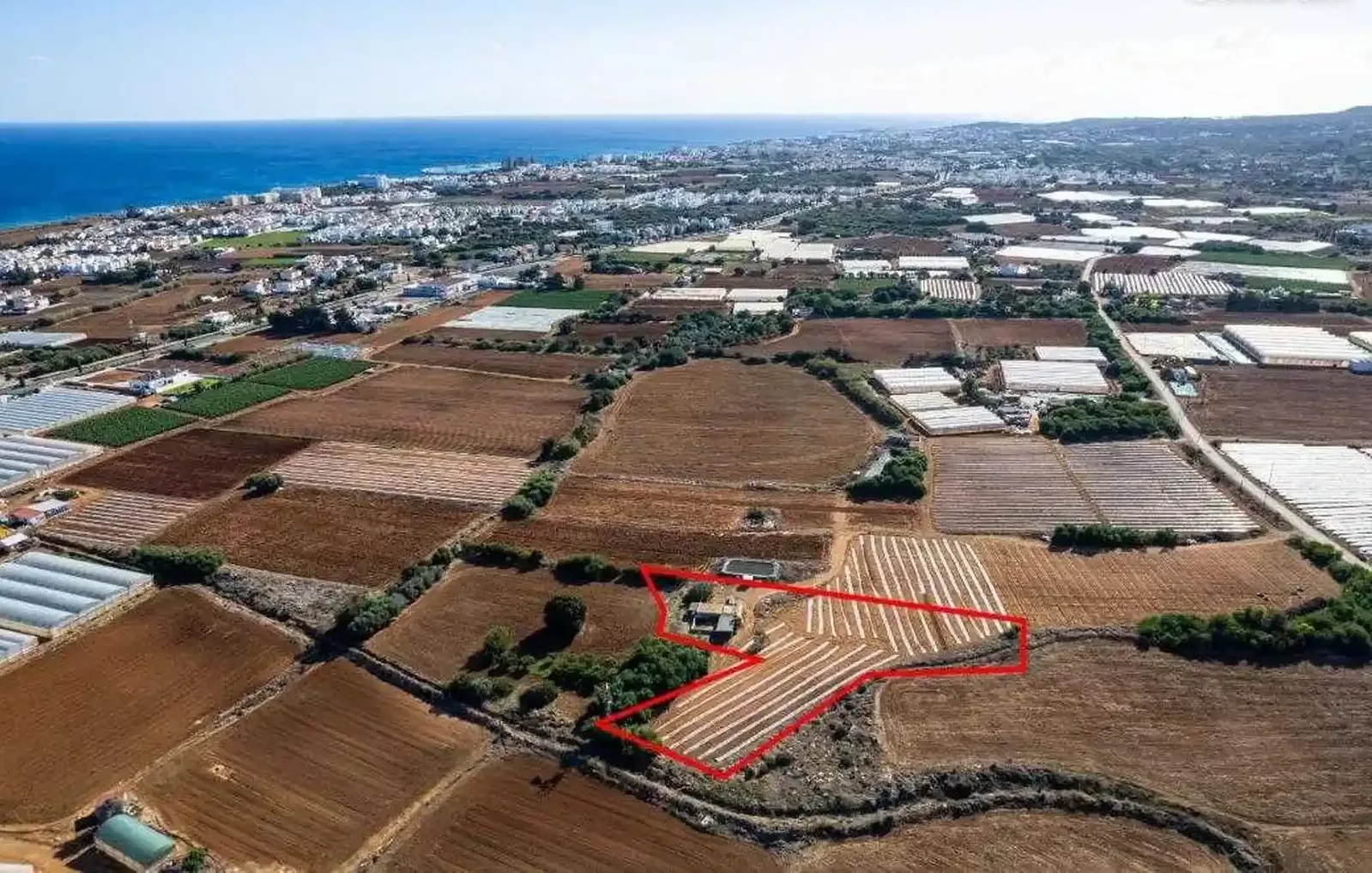
The Cyprus real estate market is expected to show steady growth in 2026, attracting investors with development and private villa construction opportunities. However, purchasing land on the island is fraught with legal and technical nuances, the most important of which is planning zones. Understanding the alphanumeric codes in official Land Registry documents determines not only the property’s value but also the feasibility of implementing your architectural design.
Contents
Basic zoning parameters in Cyprus
Before analyzing specific codes, you should understand four key indicators that govern the development of any plot of land in Cyprus. This information is included in the title deed or can be accessed through the government’s online platform, DLS:
- Building Density (Building Ratio): Determines the maximum total floor area of a building relative to the lot area. For example, at a density of 90% on a 1,000 m² lot, you can build a building with a total floor area of 900 m².
- Coverage (Coverage Ratio): Indicates the percentage of land that can be occupied by the building footprint (foundation). If the ratio is 50%, then for every 1,000 square meters of land, the house can occupy no more than 500 square meters.
- Floors: The maximum number of floors allowed.
- Height (Висота): The maximum height of the building in meters.
Below are the characteristics of the most popular zones that investors encounter when purchasing land for residential construction.
| Area code | Purpose | Density | Coverage | Floors | Height (m) |
| H1 | Residential (villages) | 120% | 70% | 3 | 11.4 |
| H2 | Residential (villages) | 90% | 50% | 2 | 8.3 |
| H3 | Residential (villages) | 60% | 35% | 2 | 8.3 |
| Ka6 | Residential (city) | 90% | 50% | 2 | 10.0 |
| Ka8 | Residential (city) | 60% | 35% | 2 | 10.0 |
| Ga3 (Γ3) | Agricultural land | 10% | 10% | 2 | 8.3 |
| Z1 (Z1) | Protected | 6% | 6% | 2 | 8.3 |
Decoding Codes: What’s the Difference Between H and Ka
When searching for a plot, you’ll notice that residential zones are marked with the letters H (from the Greek “Hierarchia”) or Ka (from the Greek “Katoikia”). The difference between them is not only terminological but also locational.
H-Series (Residential) Zones
These zones are usually located within the administrative boundaries of villages and settlements.
- H2 is the “gold standard” for private villa construction. Its 90% density allows for efficient use of the plot area, leaving room for a garden and pool.
- H4 and H5 have much lower rates (40% and 30% respectively), making them less attractive for dense developments but ideal for secluded residences.
Zones Ka series (Residential – Continuous Development)
Codes Ka6 , Ka7 , Ka8 are more common within the boundaries of large cities (Limassol, Paphos, Larnaca) or in their immediate suburbs.
- In the Ka6 zone , construction of modern residential complexes or townhouses is permitted.
- The main difference from rural areas lies in infrastructure requirements: in urban areas, access to central sewerage, road width, and the presence of sidewalks are more strictly controlled.
The dangers of buying plots with codes Ga (Γ) and Z (Z)
One of the most common mistakes made by inexperienced buyers in 2026 remains the purchase of cheap land labeled Ga3 or Z1 .
Zone Ga3 (Γ3) is agricultural land. In 2026, the development regulations for such land became even stricter. To obtain a planning permit for a house on such land, you must own a plot of at least 4,000 m² and prove that you are engaged in agricultural activities, or obtain a special permit “under exceptional circumstances,” which is practically impossible for a foreigner in Cyprus today.
Z1 (Z1) zone is a conservation area. Construction here is either completely prohibited or restricted by a coefficient of 1-6%, making the land effectively uninhabitable. Such land is often sold with a “sea view,” but without access to electricity and water.
Pre-transaction site inspection checklist for 2026
To avoid buying land that is unsuitable for building, you must follow these steps:
- Title Deed Check: Make sure the Zone field is set to a residential code (H, Ka, Eb).
- Road Access Analysis (Registered Road): If the property is not adjacent to a registered public road, you will not receive planning permission. Purchasing a property “without a road” will require a complex procedure to obtain a right-of-way through adjacent land.
- Utilities: In 2026, the cost of connecting electricity and water to remote areas could reach €20,000–€50,000. Check the proximity of the nearest connection points.
- Notes/Encumbrances: The cadastral extract must not contain any notes regarding “Green Area” (a part of the land to be given over to public greening) or “Road Widening” (alienation of a part of the land for widening a road).
- Topographical plan: Be sure to order an up-to-date topographic survey to correlate the actual boundaries with the cadastral ones.
Tax aspects and additional costs
When purchasing land in Cyprus, you must consider not only the cost of the property itself, but also the associated fees:
- VAT: When purchasing land for development, if the seller is a legal entity (developer), VAT is charged at a rate of 19%.
- Transfer Fees: If the transaction is subject to VAT, there is no title transfer fee. If there is no VAT, a progressive rate of 3% to 8% applies.
- Stamp Duty: abolished from 2026.
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions
Is it possible to change the zone of a plot from agricultural to residential?
The rezoning process is only possible as part of the Local Plan review, which is conducted by the state every few years. A private individual cannot rezone their property upon request. You can only file an objection during a public hearing if you have compelling urban planning justifications.
What is the difference between H2 and H3 for a private developer?
The difference lies in the development intensity. In the H2 zone , you can build a house up to 90% of the land area, while in the H3 zone, only up to 60%. Therefore, to build a 200 m² villa in the H2 zone , a plot of 225 m² is sufficient, while in the H3 zone, a minimum of 335 m² is required.
What is a “Green Area” on a site plan?
This is a requirement of urban planning regulations, according to which a developer, when dividing a large plot of land into smaller lots, is required to allocate up to 10-15% of the area for public green spaces. When purchasing an already allocated plot, ensure that its net plot area (NPA) is not reduced by such areas.
How to check a plot’s area online yourself?
You you can take advantage of The DLS Portal (Department of Lands and Surveys). You’ll need the Sheet number, Plan number, and Plot number. The system will display the current zone, development and coverage factors, and the number of floors.
Is it possible to build on a plot with code Ga3 if its area is less than 4,000 m²?
By 2026, this is practically impossible. Previously, there were loopholes for building on plots of 2,000 square meters or larger under special conditions, but Cyprus’s current policy is aimed at limiting residential sprawl on agricultural land to preserve the island’s natural resources.