23.09.2022
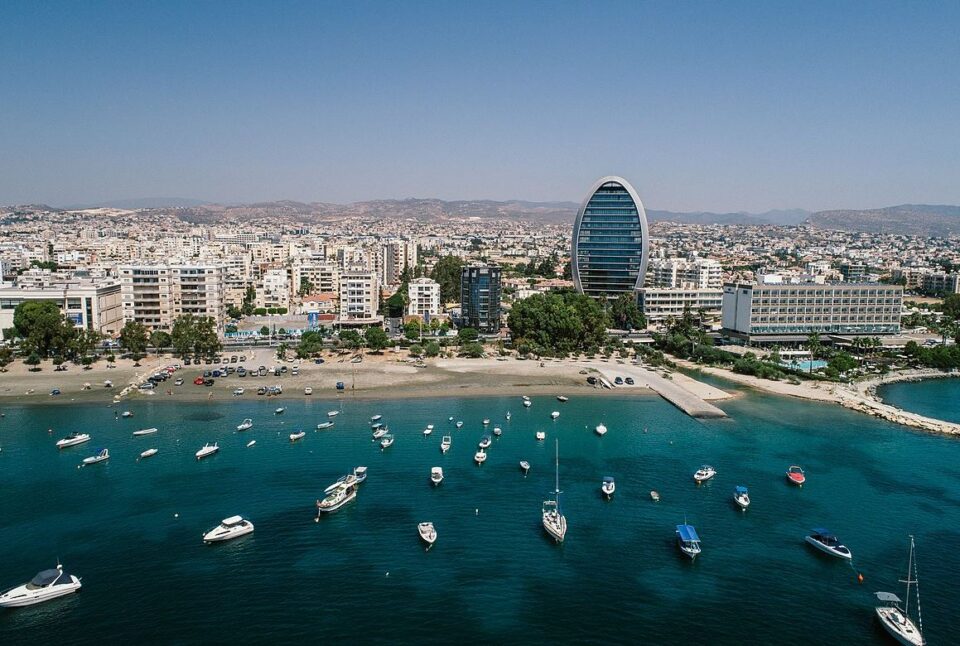
The Central Bank of Cyprus (CBC) on Thursday said that the main macroeconomic indicators of the Cypriot economy for 2022-2024 are favorable in line with its medium-term forecasts, which were published this month.
According to the central bank, despite the war in Ukraine and subsequent international sanctions imposed on Russia, the Cypriot economy recorded a strong growth of 6% in the first half of 2022, with the effects of the war expected to be more pronounced in the second half of this year. and 2023.
The central bank said that the downward revision of the external environment outlook, which is also the result of disruptions in international energy markets, had a negative impact on the consumer and business climate. As a result, the eurozone economy is expected to remain stagnant later this year and also during the first quarter of 2023. This, in turn, will affect the domestic market of Cyprus.
In addition, a significant increase in energy prices is expected to reduce the purchasing power of household incomes, which, combined with higher interest rates, will have a negative impact on domestic demand, despite the use of savings accumulated through the pandemic.
Also, despite a slight easing, disruptions in the supply chain of raw materials and goods continue to affect economic activity and push up prices, which are expected to gradually correct in 2023.
As for the economic growth rate for 2022, the central bank said it is expected to rise to 5.5%, the same as in the previous year, with GDP growth expected to come mainly from domestic demand, including investment. and private consumption, but also a faster-than-expected recovery in the tourism industry.
Moreover, the central bank clarified that the projected resilience of domestic demand is driven by prescribed investment, the reopening of the economy after the detrimental peak of the pandemic, and, in part, a recovery in private consumption as a result of drawing on their savings.
The upward revision of 2.8 percentage points in 2022 compared to June 2022 projections is mainly due to stronger-than-expected economic performance in the tourism sector.
Another factor in the improvement in economic performance was the contribution of the information technology and communications sector, which was also facilitated by the growth in the use of international technologies in Cyprus.
GDP is expected to grow to 2.5% and 3.1% in 2023 and 2024, respectively, with a downward revision from previous forecasts due to the unfavorable external outlook, including the negative effects of the looming protracted Russo-Ukrainian war, and also some medium-term impacts, mainly in professional services.
Unemployment is expected to fall to 6.7% of the workforce in 2022 from 7.5% in 2021, a slight downward revision of 0.2 percentage points from the June 2022 forecast.
This is due to greater-than-expected labor market tensions and the expected manageable impact of the war, as shown by the European Commission’s recent monthly surveys of employment expectations for the next three months.
In addition, a downward trend is projected in subsequent years, with unemployment reaching 6.5% in 2023 and then reaching 5.9% in 2024, with an upward revision from previous forecasts of 0.2 percentage points. points per year is due to the downward revision of the GDP forecast in 2023 and 2024.
As for inflation, which is related to the Harmonized Consumer Price Index (HICP), the central bank said it is expected to increase significantly in 2022, rising to 8.4% from 2.3% in 2021. It is expected to remain above or close to 9% in the remaining months of this year.
An upward revision of 1.4 percentage points from the June 2022 forecast is primarily attributable to higher energy prices, demand-side pressure on some services due to economic recovery from the peak of the pandemic, supply chain disruptions, and as a tighter-than-expected labor market.
As in previous forecasts, inflationary pressures are projected to gradually normalize in 2023 and 2024, with inflation reaching 3.9% and 2.1%, respectively. In addition, the subsequent slowdown in the HICP in subsequent years is due to the projected gradual correction in oil and food prices, as well as the stability of long-term inflation expectations.
In terms of core inflation, that is, inflation excluding energy and food, it is expected to rise to 5.1 percent in 2022 from 1.3 percent in 2021, and in 2023 is projected to fall to 2.9 percent and 2.3 percent. 2024 respectively. This is mainly due to the expected but gradual normalization of supply chain disruptions due to the demand impact of the recent interest rate hike.
The increase in forecasts for June 2022 is due to the indirect impact of higher energy prices due to the lagged impact on subcategories of inflation, as well as the resilience that the labor market is expected to continue to show.
Regarding the possibility of a deviation from the baseline forecast scenario, the central bank said that the main risks of a decline in GDP are related to the possibility of a larger-than-expected negative impact on the export of services due to the protracted war, as well as the associated impact on the external environment. They are also associated with higher-than-expected commodity and product prices due to the ongoing effects of supply chain disruptions.
Finally, with regard to inflation, the risks of rising inflation are mainly associated with higher-than-expected oil prices, as well as prolonged disruptions in global supply chains.
In 2024, the main growth risks include a possible wage and price spiral and the possibility of higher long-term inflation expectations.